Bulk Redirect Chain Checker
Paste URLs, **check redirect hops in bulk**, and export. See hop count, full chain, final destination, and response time.
| URL | Hop Count | Redirect Chain | Final URL + HTTP | Time (ms) |
|---|
- We use HEAD to read Location headers, then GET (range 0-0) if HEAD is blocked.
- Loop protection + 10 hop cap for stubborn cases.
- CSV includes chain as 301 https://a → 302 https://b → 200 https://c.
The Bulk Redirect Chain Checker instantly analyzes redirect hops and loops across multiple URLs. It helps SEOs, developers, and marketers track 301s, 302s, and final destinations to ensure every link flows cleanly without losing link equity or speed.
What the Bulk Redirect Chain Checker Does
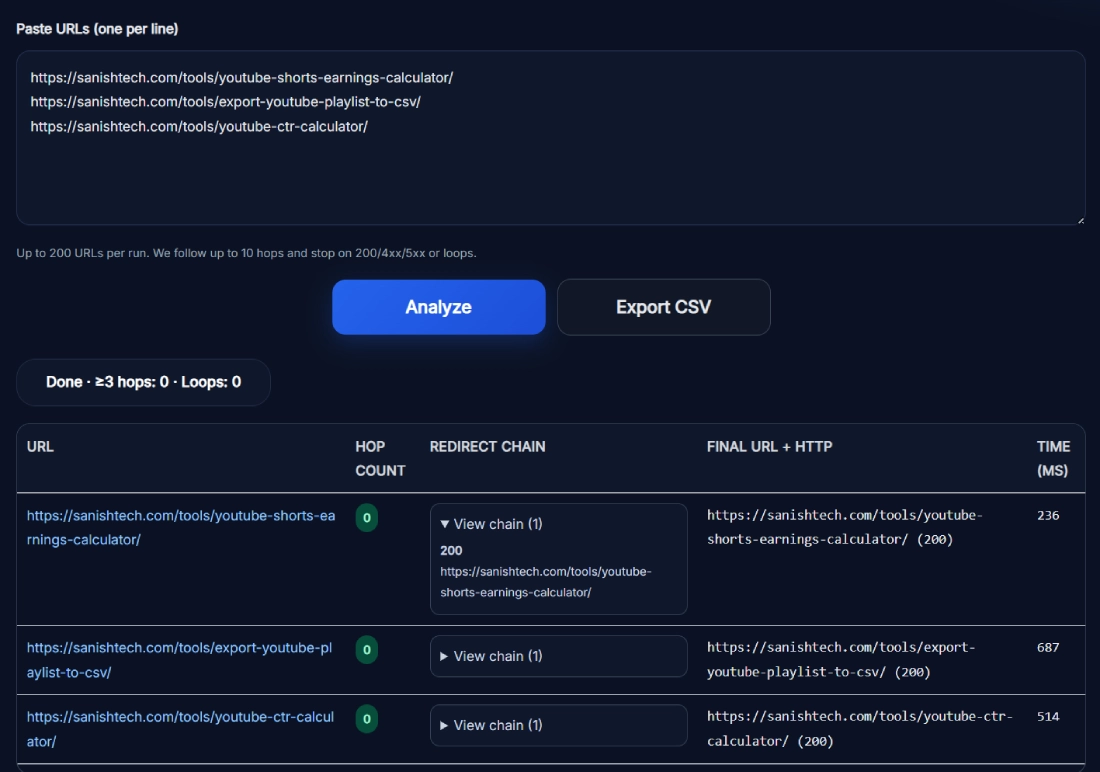
This tool digs deep into how your URLs redirect behind the scenes. It detects every hop in a redirect chain, shows where each link ends up, and flags any redirect loops that can break user experience or hurt SEO. You’ll see hop counts, redirect types, final URL status (like 200 OK), and exact response times in milliseconds.
The moment you paste your URLs and click Analyze, the tool starts testing each link’s journey from source to final destination. Whether you’re auditing a single site or hundreds of URLs, you’ll get a complete redirect map in seconds. If you want to validate the final destination response codes and SSL in one pass, pair your results with the Bulk HTTP Status Checker.
Key Features of Bulk Redirect Chain Checker
Here’s what makes this redirect audit tool stand out:
- Detects long or unnecessary redirect chains instantly.
- Displays HTTP codes like 301, 302, 307, 404, or 200 clearly.
- Prevents infinite loops with built-in hop protection (max 10 per chain).
- Shows total response time (in ms) for quick performance insight.
- Exports complete redirect data to CSV for client or internal reports.
- Works with up to 200 URLs per batch — perfect for agency audits.
- Minimal server load, runs directly in your browser without login.
It’s fast, free, and designed for practical SEO diagnostics rather than fancy charts you’ll never use. Once you fix redirect issues, it’s smart to confirm canonical consistency with the Bulk Canonical Checker so your preferred URLs aren’t pointing into redirect paths.
How to Use the Bulk Redirect Chain Checker Tool
The UI is clean, dark-themed, and ridiculously easy to use. Follow these quick steps:
- Paste URLs (one per line): Drop in up to 200 links from your site, sitemap, or spreadsheet. If you’re pulling URLs directly from an index, grab the full list first using the XML Sitemap URL Extractor.
- Click “Analyze”: The tool runs redirect tests and shows results below.
- View redirect chains: Expand “View Chain” to see every hop, whether it’s a 301, 302, or meta refresh.
- Check final URL + HTTP: The rightmost column shows the resolved URL with its status (for example: https://sanishtech.com/tools/youtube-ctr-calculator/ (200)).
- Export CSV: Hit Export CSV to download all data — URL, hops, chains, and response time — ready for client reporting.
Below the result section, you’ll see a small status line:Done: >3 hops • Loops: 0 — which confirms the audit completed without endless redirects.
Why Checking Redirect Chains Matters for SEO
Redirect chains might seem harmless, but they quietly erode your site’s technical health. Each hop adds latency, burns crawl budget, and reduces the chance of Google passing full link equity. Imagine a user landing on an outdated URL — if it hops three times before reaching the live page, you’ve already lost a chunk of your site’s authority and speed.
By running regular audits with this redirect audit tool, you can catch these problems before they spiral. It helps you:
- Simplify chains by keeping a single 301 to the final destination.
- Avoid duplicate redirects from old HTTPS migrations.
- Detect unnecessary 302s that never got updated.
Fixing redirect issues often results in a visible boost in crawl efficiency and organic ranking stability. After cleanup, it’s worth checking your internal linking targets with the Free Internal Link Checker Tool so important pages aren’t still pointing to redirected URLs.
Real Example of Redirect Audit with This Tool
Let’s say you’re checking this URL:http://example.com/old-blog-post
The Bulk Redirect Chain Checker might show this result:
- http://example.com/old-blog-post → 301 → https://example.com/old-blog-post
- https://example.com/old-blog-post → 301 → https://example.com/blog/seo-tips
- Final: https://example.com/blog/seo-tips (200)
That’s two redirects before reaching the real article. It’s not terrible, but ideally you’d update the first link to point directly to the final destination. Over hundreds of URLs, these micro-fixes shave seconds off load time and help bots crawl your site faster.
Benefits of Using This Redirect Audit Tool
This isn’t just another SEO gadget — it’s a real-world time-saver for:
- SEO agencies: Run bulk audits and send exportable CSV reports to clients showing full redirect flow and response timing.
- Developers: Quickly spot broken redirects, loops, or outdated URLs during site migrations.
- Bloggers & site owners: Test affiliate links, external references, and social share URLs to ensure they resolve properly.
- Webmasters: Ensure all 301 and 302 redirects comply with SEO best practices.
Because everything happens client-side, you get instant visibility without sending data to third-party servers. For quick page-level validation of metadata on final URLs, you can also run the Meta Tag Analyzer Tool on priority pages after redirect cleanup.
Pro Tips for Getting the Best Results
- Limit each batch to under 200 URLs for fastest response time.
- Re-run audits after changing redirect rules or migrating domains.
- Pay attention to long chains (>3 hops) — they’re often unnecessary.
- After export, filter CSVs by “Hop Count” column to prioritize fixes.
- Keep your redirect maps updated in a spreadsheet for client handovers.
And hey, don’t forget to double-check affiliate URLs too — some tracking redirects can silently eat your referral credit.
FAQ – Bulk Redirect Chain Checker
How many URLs can I analyze at once?
You can analyze up to 200 URLs per run. For larger sites, simply break your list into smaller batches to keep processing quick and stable. The export option makes it easy to merge data later in a spreadsheet.
Does this tool detect redirect loops automatically?
Yes. The tool stops scanning once it detects a loop and labels it under “Loops.” This prevents endless checks and helps pinpoint circular redirects that often appear after misconfigured 301 chains.
Can I export redirect chains for client reporting?
Absolutely. The Export CSV button lets you download a structured file containing URL, hop count, redirect chain, final URL, and response time — ideal for agency deliverables or migration audits.
What redirect types are supported?
It supports 301, 302, 303, 307, and 308 redirects, along with basic meta and JavaScript redirects. You can also view the final HTTP response code like (200 OK) for each destination.
How does the redirect audit tool calculate response time?
It measures the time taken in milliseconds to resolve each redirect chain from start to finish, helping identify latency issues caused by slow redirects or chained hops.
What is a redirect chain in SEO?
A redirect chain occurs when one URL redirects to another, which then redirects again, forming a sequence of hops before reaching the final page. These chains can reduce link equity and slow down crawling.
Why should I fix multiple redirects?
Because each redirect slightly delays page loading and weakens the link signal. Fewer hops mean faster pages, better crawlability, and improved user experience — all ranking factors Google values.
Does Google follow long redirect chains?
Yes, but only up to a point. If chains become too long or inconsistent, Google may stop following them, which can prevent pages from being indexed or ranked properly.
How can I check redirect chains online for free?
Use this tool. Just paste your URLs, click Analyze, and view each hop instantly. No signup or installation needed — it’s 100% browser-based.
What’s the difference between 301 and 302 redirects?
A 301 is a permanent redirect that passes SEO value to the target page, while a 302 is temporary and doesn’t fully transfer ranking signals. Always use 301s for long-term changes.
